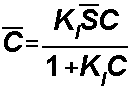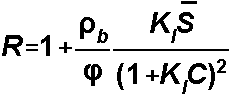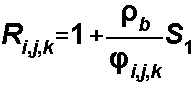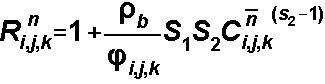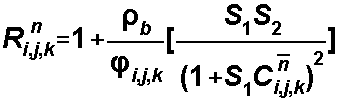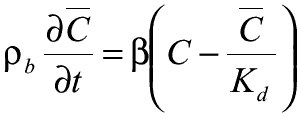ADSORPTION:
MT3D allows 3 options for adsorption isotherms and uses
them to reduce the velocity term in the solution through the retardation factor
as follows:
Linear Isotherm
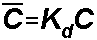
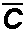 is the sorbed concentration
is the sorbed concentration

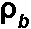 = dry bulk density
= dry bulk density
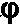 = effective porosity
= effective porosity
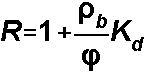
Freundlich
isotherm:
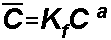
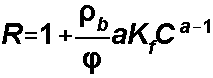
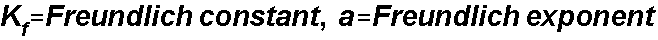
Langmuir isotherm:
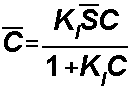
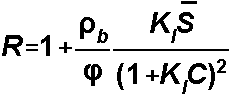

********************************************************************
To define adsorption in MT3D the user specifies:
********************************************************************
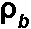 = dry bulk density
= dry bulk density
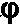 = effective porosity
= effective porosity
S1 and S2
For the Linear
Isotherm, S1 = Kd
and S2is not used:
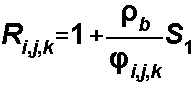
For the Freundlich Isotherm, S1
= Kf and S2is a, the Freundlich
exponent:
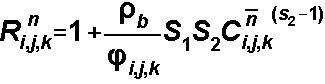
For the Langmuir Isotherm, S1
= Kl and S2is the total concentration of sorption sites:
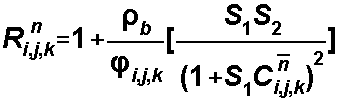
Non-equilibrium Sorption is represented as a first-order reversible kinetic reaction:
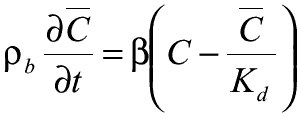
 = first-order mass transfer rate between
dissolved and sorbed phases
= first-order mass transfer rate between
dissolved and sorbed phases
Kd = distribution coefficient for the sorbed phase
As 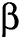 increases,
the mass transfer rate increases and approaches the equilibrium-controlled linear
sorption
increases,
the mass transfer rate increases and approaches the equilibrium-controlled linear
sorption
![]()
![]() is the sorbed concentration
is the sorbed concentration
![]() = dry bulk density
= dry bulk density ![]() = effective porosity
= effective porosity 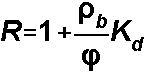
![]()
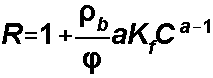
![]()