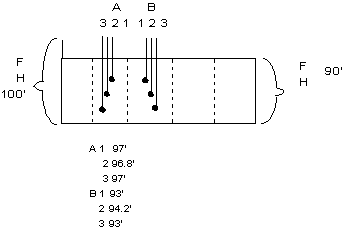
One example of how measurements of independent variables reveal caharcterisitcs of a system that are not detected by measurments of parameter values.
The following model was constructed with
no recharge
and a homogeneous K, using a value interpreted from a small scale aquifer test
conducted to the right of B. Heads in the nested piezometers, A and B, are known
and do not match the simulated values (in the model, the
dashed lines of equal head are vertical and range from 98' on the left to 92'
on the right).

1) The head data indicate that adding a high K lens between piezometers A and B would cause heads in the nested piezometers to be more like the field observations, thus heads can provide clues to variations in geology (and associated hydraulic properties) even when the borings do not penetrate the geological variations.
2) In addition, consider that the specific value of K estimated from the aquifer test may reflect minor heterogenetities near that well bore and not the effective K of the entire section. In this case, if we also had a measurement of the flow rate from the right side of the system, we could better estimate the effective K.