Calculate the contaminant concentration at the same time and location, i.e.:
in a ground-water sample collected from a well 15 meters down gradient after
1 year. The well has a total depth of 14 meters and is screened from 13 to 14
meters depth. The well is offset laterally from the center of the tank by a
distance of 5 meters. When you want to confirm your answer, click answer
for the value.
For your convenience, I include the appropriate expression here:
(Domenico
1987 - An analytical method for multidimensional transport of a decaying contaminant
species - Journal of Hydrology, v. 91, p. 49-58)
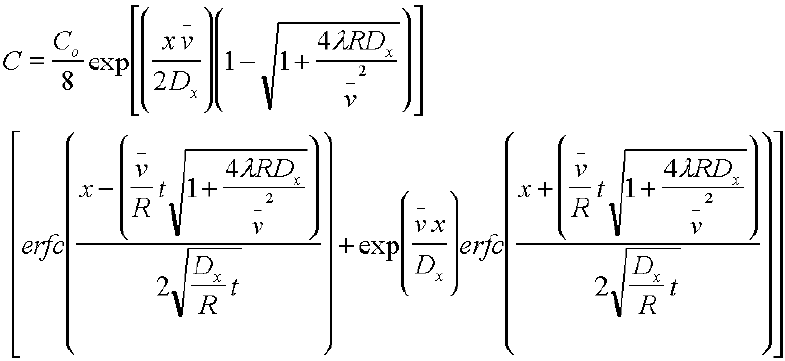
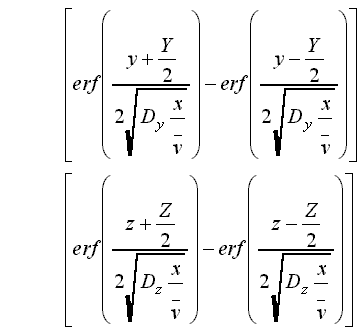
where:
Co = source concentration [M/L3]
C = concentration [M/L3]
x = distance from the source in the direction of flow
y, z = orthogonal distances from the center of the plane source
![]() = average linear velocity
of ground water [L/T ]
= average linear velocity
of ground water [L/T ]
t = time since continuous concentration release began [ T ]
Dx, Dy, Dz = dispersion coefficients in the
x, y, & z directions [L2/T ]
erf
= the error function ERF
erfc = the complimentary error function ERFC
FOR DOWNWARD SPREADING ONLY, substitute Z for Z/2
FOR NO SPREADING IN THE z DIRECTION, increase CO/8
to CO/4 and omit the erf terms for z.
Calculate your answer, being extremely careful with respect
to using consistent units and noticing how the answer is expressed (e.g. as
Concentration or relative Concentration, then check
yourself by deciding whether the answer is reasonable, by visiting the key.
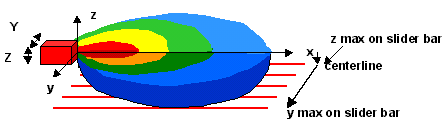
Calculate your answer, being extremely careful with respect
to using consistent units and noticing how the answer is expressed (e.g. as
Concentration or relative Concentration, then check
yourself by deciding whether the answer is reasonable, and visiting the key.
KEY TO EXERCISE FOR EXPLORING 3D CONTAMINANT TRANSPORT, CONTINUOUS SOURCE with SORPTION and DECAY