EENG 383
Lab 9 - Signal acquisition| Lab: | 9 |
| Status | Live |
InLab 9
Some self guided activities.Lab 9 assignment
Create an embedded application that writes audio data to the SD Card that, in the next lab, will be played back through the speaker. The general architecture of the lab is shown below. You will use an ISR to collect microphone samples and store them in one of two buffers, the blue buffer in the figure below. While samples are being stored in the blueBuffer, the redBuffer is being sent out to the SD Card over the SPI but through the SDCARD_WriteBlock interface function supplied in this inLab. Once blueBuffer is full and the redBuffer has been sent, their roles are swapped. The blueBuffer is then sent to the SD Card and, while this is being done, new microphone samples are sent to the redBuffer. This is called double buffering and an important technique in signal processing.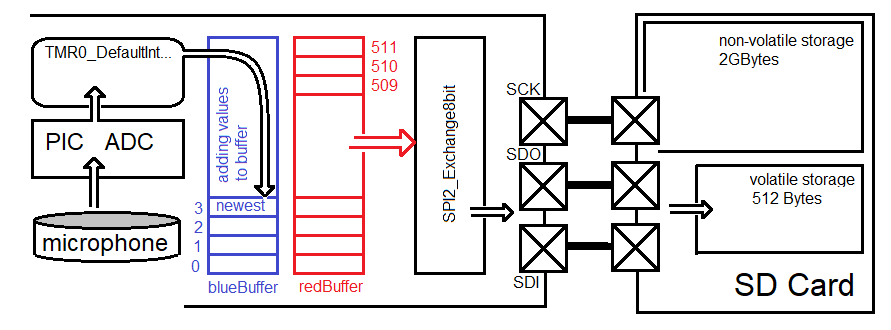
Software
At start-up your program should present a splash screen - this would be a great place for some ASCII art. The splash screen should also contain connection instruction for the development board; for this assignment tell the user there are no jumpers to install! When you press "?" at the terminal you should be greeted with the following menu.------------------------------------------------- ?: help menu o: k Z: Reset processor z: Clear the terminal ------------------------------------------------- i: Initialize SD card ------------------------------------------------- a/A decrease/increase read address r: read a block of 512 bytes from SD card 1: write perfect 26 value sine wave to 128 blocks ------------------------------------------------- +/-: Increase/Decrease the sample rate by 10 us W: Write microphone => SD card at 1600 us s: spool memory to a csv file -------------------------------------------------
- ?
Prints out the ever useful help menu.
- Z
Reset the processor so that we can see that splash screen.
- z
Clear the terminal using a bunch of new lines.
- i
Initialize the SD Card using the routines given in the inLab code.
- r
This should read a block from the SD CArd and display it to the terminal just as was done in the inLab code - just cut-and-paste.
- a/A
decrement or increment the address used to read the memory. This is also a cut-and-paste from the inlab code.
- 1
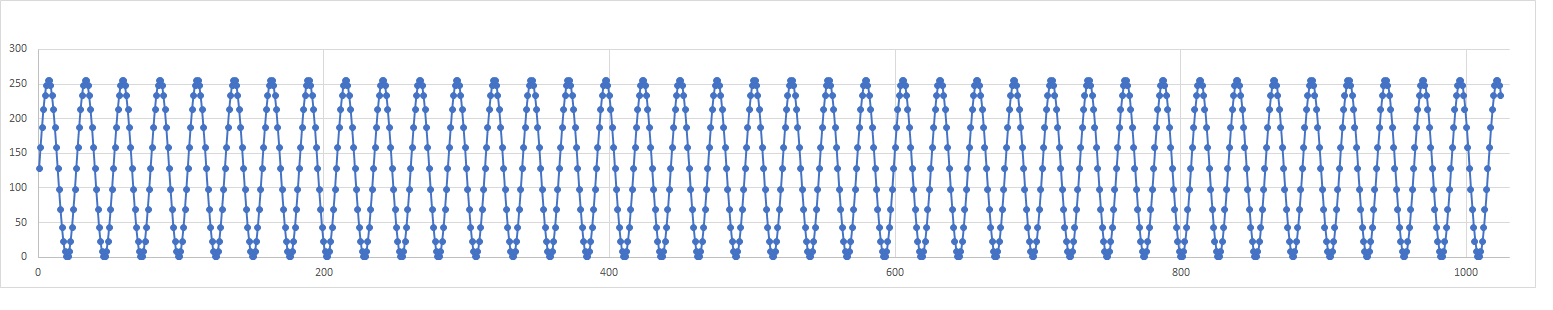
In order to test next weeks program, it will be very helpful to have a known waveform stored in the SD Card. Let's do future you a favor and take care of this now. Copy the following sine wave over and over again in the SD Card. You need to copy the wave "smoothly" across block boundaries. In other words, when your code runs out of room in one block at sin[index], the first value stored in the next block should be sin[index+1], NOT sin[0]. Continue storing sine waves until the user presses any key. After a keypress, tell the user how many blocks have been stored.const uint8_t sin[SINE_WAVE_ARRAY_LENGTH] = {128, 159, 187, 213, 233, 248, 255, 255, 248, 233, 213, 187, 159, 128, 97, 69, 43, 23, 8, 1, 1, 8, 23, 43, 69, 97};To test this function, store at least 2 blocks worth of sine waves, then use the 's' function and spool out at least 2 blocks worth of data to verify that the sin wave smoothly crosses the block boundry. In other words, the sine wave should have no discontinuity when crossing the block boundry.
You need to insert a delay beteen consectutive block writes for the "1" function. I did this by placing a TMR1 delay loop after the each call to SDCARD_WriteBlock. I configured TMR1 to run with a 1:8 prescaler.for (blockCount = 0; blockCount < MAX_NUM_BLOCKS; blockCount++) { \\for loop to fill the redBuffer with 512 sin wave samples SDCARD_WriteBlock(loopSDcardAddress, redBuffer) while ((status = SDCARD_PollWriteComplete()) == WRITE_NOT_COMPLETE); // Slow down the write sequence to insure that blocks are written TMR1_WriteTimer(0x0000); PIR1bits.TMR1IF = 0; while (PIR1bits.TMR1IF == 0); } // end for blockCountNote, do NOT do this in the "W" function. The aquisition of the samples takes 51.2 ms which is more than enough time between SDCARD_WriteBlock calls.
- +/-
Change SAMPLE_RATE from a #define to a global variable sampleRate. Initialize the sampleRate to generate an interrupt every 100µs. Allow the '+' function the increase the sampleRate by 10µs and the '-' function the decrease the sampleRate by 10µs. Do not allow the sampleRate to go below 20µs.
- W
This will record the microphone values converted through the ADC into the SD Card at the sampling rate (default to 100 us). When the user types 'W' in the terminal window, prompt with user with Press any key to start recording audio and press any key to stop recording.. This will allow the user to get all set-up without having to pay attention to which key they press in order to start the audio recording.
Your program must use double buffering so that it can acquire new samples while storing old samples. To do this you will use the TMR0 ISR to collected converted values from the ADC and start a new conversion. In addition, the TMR0 ISR is responsible for moving the sampled value into either the red or blue buffer (both global variables because of their size), and set flags true to indicate when either buffer is full. Main should be monitoring these flags and writing the red or blue buffer to the SD Card when either is full. While main is doing this, the ISR should be storing microphone samples to the other buffer.
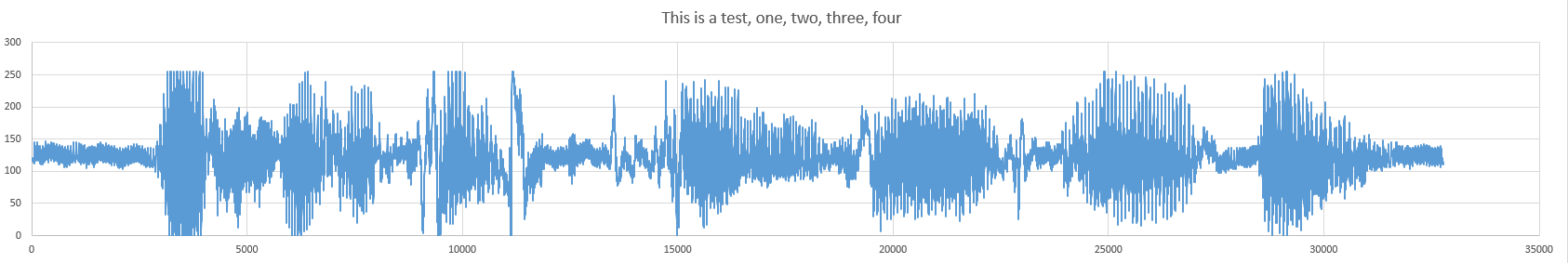
You should record "This is a test, one, two, three, four". Then spool the audio message the 's' function. Then plot this waveform using the Excel Instructions below.
Consider trying our Husker Scope to record clean audio waveforms with predictable shapes. - s
In computing the term spooling is generally taken to mean outputting a lot of raw data. I want you to provide the capability to spool blocks of the SD Card to the terminal. Before you start spooling, you will configure PuTTY to store anything that appears on the terminal into a file. You will then spool blocks of the SD CArd to the terminal. Finally you will instruct PuTTY to close the file. You will then open the file in Excel and plot the audio data. I have found spooling to be slow, it may be worth increasing the Baud rate for this assignment - if you do, don't forget to configure PuTTy to the same Baud rate.
When the user presses "s", provide them with the following prompt:You may terminate spooling at anytime with a keypress. To spool terminal contents into a file follow these instructions: Right mouse click on the upper left of the PuTTY window Select: Change settings... Select: Logging Select: Session logging: All session output Log file name: Browse and provide a .csv extension to your file name Select: Apply Press any key to start
Your program should then read consecutive blocks of the SD Card and print the ADC values, one per row, out to the terminal. After each block is printed to the terminal, check if a key has been pressed, if not continue to read that block, print all 512-bytes and then check again for a keypress. You can check for a keypress using the EUSART1_DataReady function - you should clear the associated flag using a void EUSART1 read using a statement like: (void) EUSART1_Read();
Continue until a key is pressed or the last byte of the last block has been printed to the terminal. At this point you should present the user with some instructions to close the log file. They should look something like:117 116 115 116 115 117 115 115 115 117 113 112 112 112 113 Spooled 512 out of the 512 blocks. To close the file follow these instructions: Right mouse click on the upper left of the PuTTY window Select: Change settings... Select: Logging Select: Session logging: None Select: Apply
Excel Instructions
In order to plot the spooled data, follow these instructions.- Open putty.csv in excel,
- Delete any non-data lines at the top of column A by selecting the row numbers, right mouse and select delete,
- Go to the bottom of the A column by clicking on any cell in the A column and then pressing the "End" key and then pressing the down-arrow key,
- Delete any non-data rows at the bottom of column A,
- Go back to the top of column A by clicking on any cell in column A and the pressing the "End" key and then pressing the up-arrow key,
- Select column A by clicking on the A,
- Add a X-Y scatter plot Insert → Charts → X-Y scatter → Scatter with Straight Lines,
- Change the title of the plot with that you said, by clicking on "title" and typing,
- Stretch the graph horizontally by grabbing the right edge and mousing right.
When you plot the first 1024 entries of the sine wave you should get something that looks like the following.
Turn-in
You may work with a single partner (or alone) to complete this lab. Submit your main.c file on Canvas using the instructions posted there. You should take note of the Rubric that will be used to evaluate your assignment. Please form a group before submitting using the instructions posted on Canvas. You will demonstrate your code at the beginning of lab.Be prepared to show the graders your Excel plot with the sine wave and audio waveform "test one, two, three".